Ransomware variant that impersonates Mexican Federal Police identity
In one previous posts on this blog, it was performed the analysis of a malware sample which goal is to get money by hijacking the user's session once the computer gets infected. It has recently been reported several ransomware cases about Federal Police to the Computer Emergency Response Team UNAM-CERT. The lock window on the computer is shown below:

The screen displayed the changes regarding to the previous versions of this malicious software type. The elimination procedure is different too, in this new version is not possible to reach to the system in failsafe mode in order to remove the malicious software.
As a new intimidation technique, the infected computer displays information as:
- Public IP address of the infected computer
- Country
- Region
- City
- ISP (Internet Service Provider)
- Operating System
- User name
The captured sample of the infected computers has the original name "skype.dat", but once it’s checked out with file tool, the file type which it belongs is identified as Windows executable file.
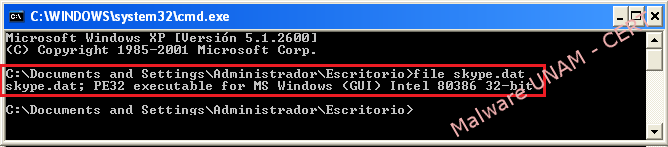
Therefore, the UNAM-CERT team proceeded to the analysis. To make it able to run it was renamed as "skype.exe".
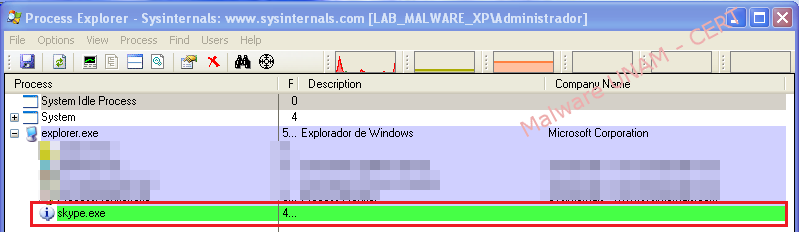
The process "skype.exe" remains active a couple of seconds and then start the "svchost.exe" process trojanized.

Approximately two minutes after the infection, the window that blocks the user session is shown, with the logo of Federal Police, information about the infected computer, the Mexican nation shield, the clauses that specify why the computer could have been blocked and the instructions of how to pay the system's kidnapping. Picturebelow shows the ransomware new window:

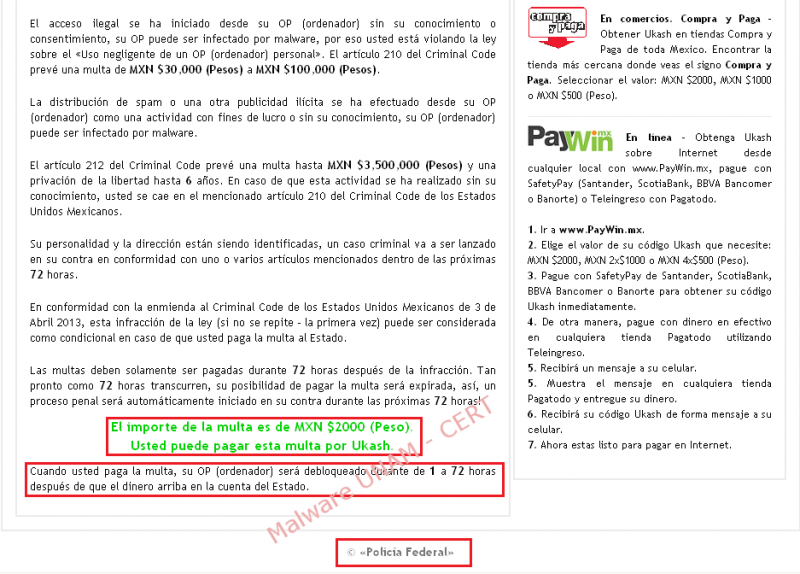
As a test, a PIN code of 19 random digits was entered to in order to see the application behavior, it was also selected the amount of 2,000 mexican pesos from the available ranges, chosing this option from another two amounts: 500 y 1,000 mexican pesos.

Once “Pay Ukash” button was pressed, is displays the following error message:
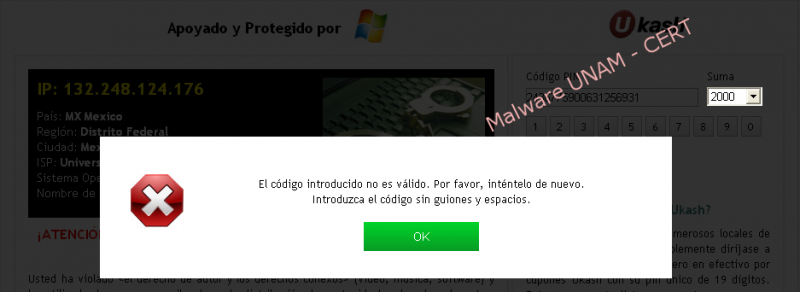
“The code entered is not valid, please try again later. Please enter the code with neither hyphen nor spaces.”
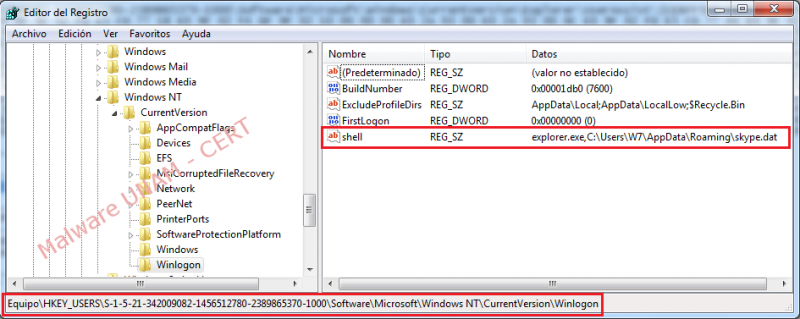
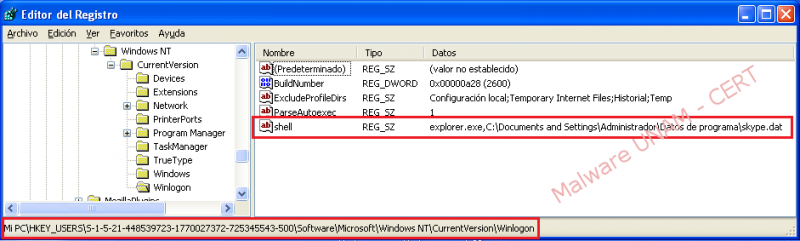
In concerning to the Windows Registry, the malware creates a key named “shell" in the path HKU\S-1-5-21-448539723-1770027372-725345543-500\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon with the following value: "explorer.exe,C:\Documents and Settings\Administrador\Datos de programa\skype.dat".
Winlogon loads the user profile when logging in, using the configuration that lets the malware start the "explorer.exe" process and by doing this, the "kpype.dat" malicious software hosted on the route C:\Documents and Settings\Administrador\Datos de programa\ starts too.

For this particular sample, the tests were performed in both Windows XP and Windows 7 operating systems, in order to regain control of the system and to take security measures related to the information stored.
How to remove this malware in Windows XP
Once that the computer has been infected, the malicious software can not start the "Start Task Manager" with the combination key CTRL + ALT + DEL, neither boot into "Safe Mode". As a solution, it’s recommended to start the system with a Linux Live CD, in our case we use the Ubuntu distribution 11.04.
- Turn on the computer, press F2 to enter the BIOS (Basic Input-Output System). Go to the tab "Boot" and change the boot order of the devices with the keys "+" or "-" making the option "CD-ROM Drive" at first.
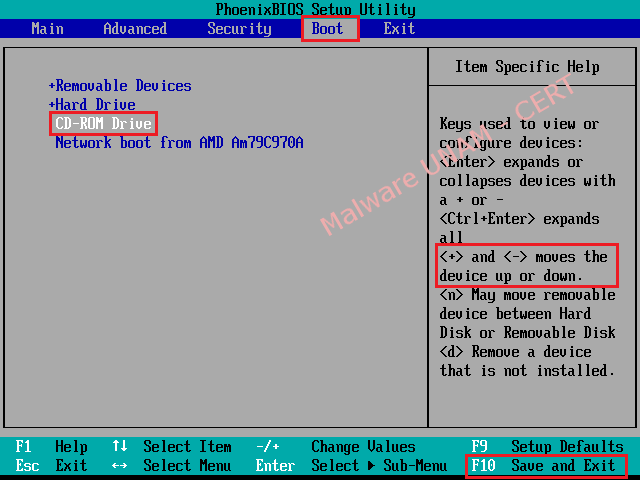
- Once you have set the boot order correctly, press the F10 key to save the changes and exit the BIOS, with this action the computer will display a confirmation message, then it’s necessary just to click in the affirmative option. Immediately, the system restarts automatically.
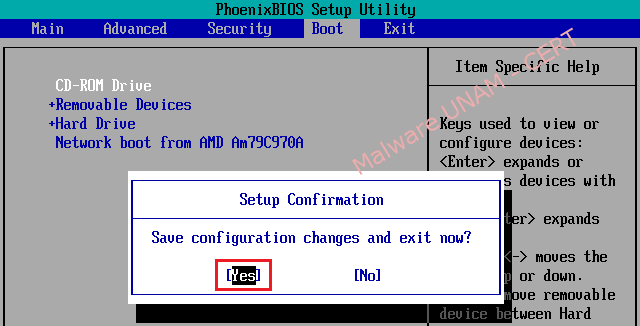
- With the Live CD into the computer, boot the "Ubuntu 11.04" operating system.

- If the user prefers, it’s possible to change the language the operating system that will be displayed, and then select the "Try Ubuntu" optionto begin the test of the Ubuntu distribution.
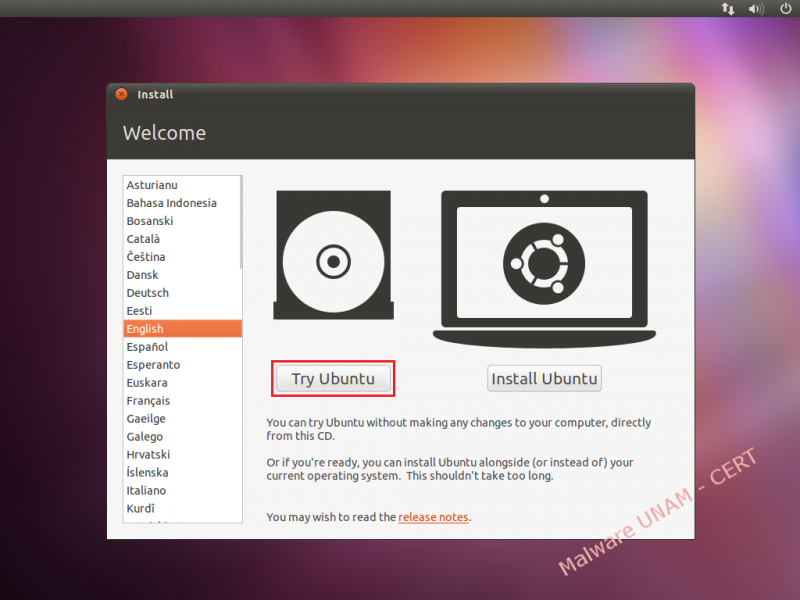
- Then it’s necessary to go to the "Places" menu and select the Windows Files System partition, in our case, is the hard drive of 27 GB.
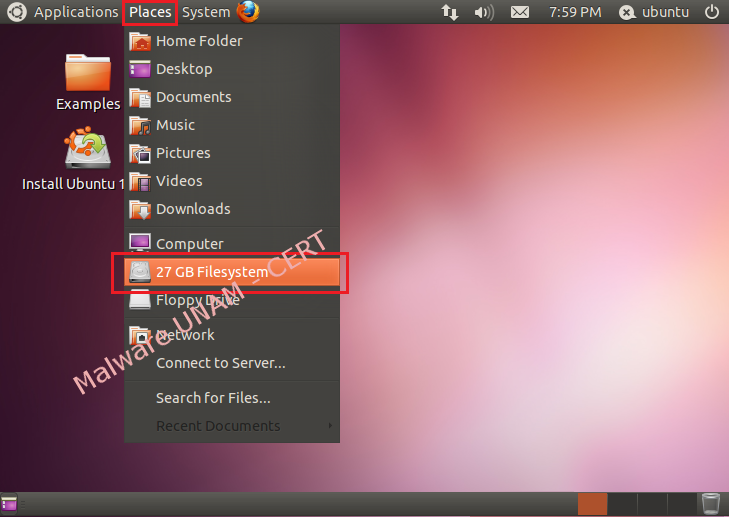
- Give double click on the newly mounted drive and go to the route "Documents and Settings" => "Administrator" (user of the infected system) => "Application Data". Then delete the files "skype.dat" and "skype.ini".
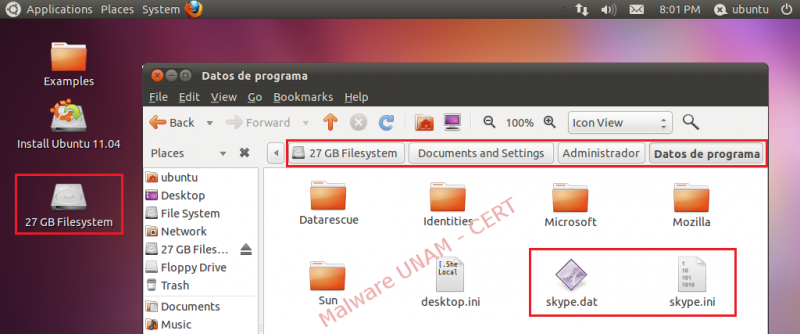
- By this moment, the threat has been eliminated, the only thing missing is to reboot the computer and start Windows ordinarily.

- With those changes made, the user profile should be not affected by the ransomware because the binary file was removed using Linux.

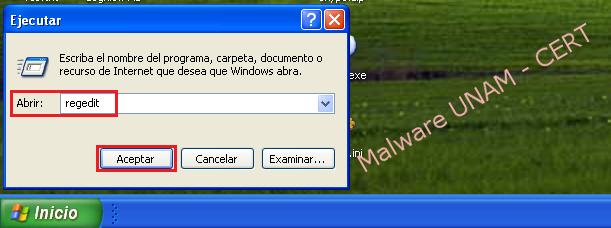
- Once the session is restarted correctly, it’s recommended to remove the registry key that generated the malware, to do this, you need to go to the "Start" menu and select "Run..."
- To open Windows "Registry Editor" you must write the "regedit" word and click on the button "OK".
- Go to the route HKU\S-1-5-21-448539723-1770027372-725345543-500\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\ and delete the registry key with the "shell" name.
- Having the threat eradicated, the system boot into "Safe Mode" is not affected.

How to remove this malware in Windows 7
To delete the malware in the Windows 7 operating system, you should carry out the same steps described for Windows XP but with the consideration of the user name, the location of the registry key and the "skype.dat" binary file.
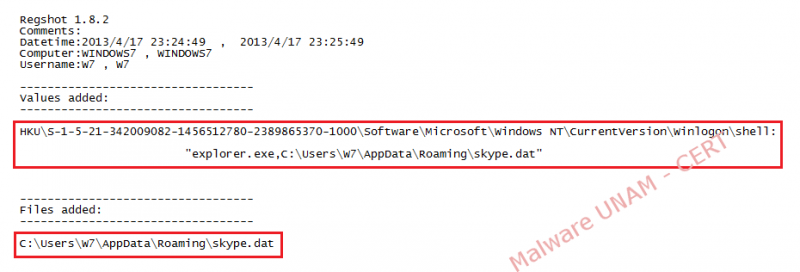
- The registry key is the next one:
HKU\S-1-5-21-342009082-1456512780-2389865370-1000\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\shell: "explorer.exe,C:\Users\W7\AppData\Roaming\skype.dat"
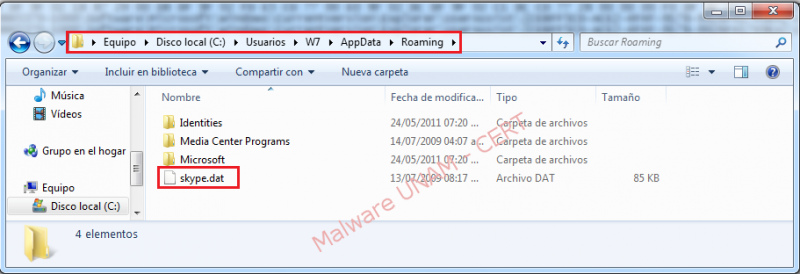
- The executable file to be deleted is located in the path:
C:\Users\W7\AppData\Roaming\skype.dat
- Finally for removing the registry key named "shell", you must go to the following path:
HKU\S-1-5-21-342009082-1456512780-2389865370-1000\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\